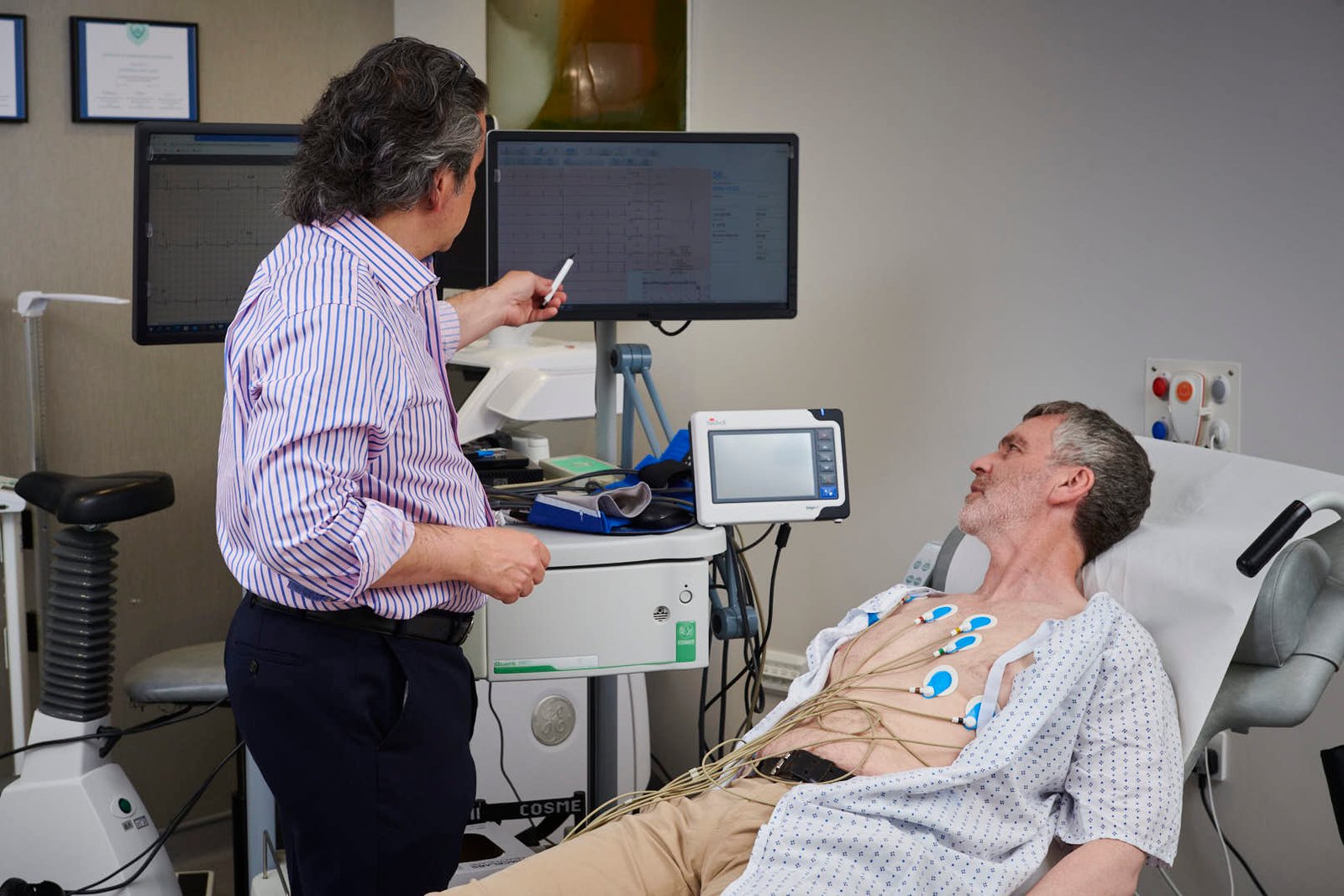
ECG
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a medical test that measures the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It is one of the most commonly used diagnostic tools in cardiology, providing vital information about the heart’s rhythm and electrical impulses.
The heart’s activity is controlled by electrical signals that prompt it to contract and pump blood. These signals originate from the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s natural pacemaker, and travel through the heart muscle, causing the heart to beat. The ECG records these signals and represents them as waves on a graph.
ECG Components
An ECG tracing typically includes several key components:
- P Wave: Represents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the atria (the upper chambers of the heart).
- QRS Complex: Represents the electrical activity associated with the contraction of the ventricles (the lower chambers of the heart).
- T Wave: Represents the repolarization (recovery) of the ventricles.
- ST Segment: The flat section between the end of the S wave and the beginning of the T wave; it can indicate issues like ischemia or heart attack if abnormal.
- PR Interval: The time between the onset of the P wave and the start of the QRS complex, representing the time taken for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
Interventions and Techniques
OT interventions are diverse and tailored to the individual’s needs. Common techniques include:
- Adaptive Techniques and Equipment: Teaching clients to use tools and devices that facilitate independence in daily activities.
- Environmental Modifications: Altering the home or work environment to enhance accessibility and safety.
- Therapeutic Activities: Engaging clients in purposeful activities that improve physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning.
- Education and Training: Providing education to clients and caregivers about managing conditions and optimizing performance in daily tasks.
Education and Professional Development
Becoming an occupational therapist typically requires a master’s degree in occupational therapy, although some regions may require a doctoral degree. Additionally, occupational therapists must pass a national certification exam and obtain licensure to practice. Continuing education is crucial in this field to stay current with the latest research and techniques.
